What is Galileo and COSPAS-SARSAT?.
Galileo is Europe’s own global navigation satellite system, providing a highly accurate, guaranteed global positioning service under civilian control. Currently providing Initial Services, Galileo is interoperable with GPS and Glonass, the US and Russian global satellite navigation systems. By offering dual frequencies as standard, Galileo is set to deliver real-time positioning accuracy down to the metre range.
What is COSPAS-SARSAT?
COSPAS-SARSAT, founded in 1979, is an international satellite-based search and rescue system designed to quickly detect and locate distress signals from emergency beacons, such as those activated by aircraft, vessels, and people who are lost or in distress. The system is a collaboration of several countries and is managed by the International COSPAS-SARSAT Programm
When a distress signal is received, it is analysed by a ground station, and the information is then relayed to the appropriate search and rescue authorities who are in charge of responding to the emergency.
The system is designed to detect 406 MHz distress signals transmitted by emergency beacons registered with the relevant authority in the country where the beacon is used.
It also uses a 121.5 MHz homing signal to help search and rescue personnel pinpoint the exact location of the distress signal. The COSPAS-SARSAT satellite system was developed collaboratively by the United States, Canada, France, Russia, and other countries and is used by search and rescue organisations worldwide, including the United States Coast Guard, the Royal Canadian Air Force, and the Australian Maritime Safety Authority. Since its commencement in 1982, the system has been credited with saving thousands of lives.
Currently, 43 countries and organisations participate in the operation and management of the COSPAS-SARSAT system. COSPAS-SARSAT also cooperates with various international organisations including the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
COSPAS-SARSAT currently has 27 operational satellites in orbit, with two more launched in 2021.
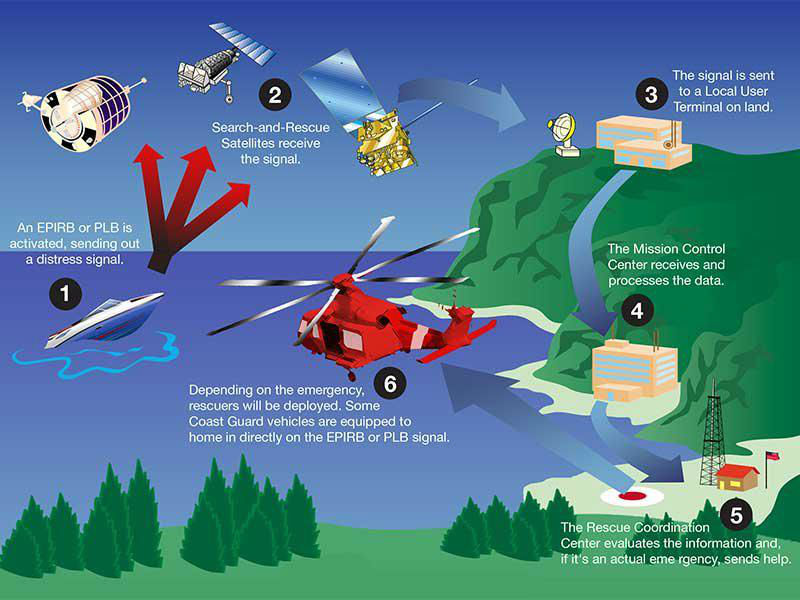
Galileo’s contribution to COSPAS-SARSAT
The Galileo SAR service is Europe’s contribution to the upgrade of COSPAS-SARSAT. The Search and Rescue Transponder on Galileo satellites picks up signals emitted from distress beacons in the 406 – 406.1MHz band and broadcasts this information to dedicated ground stations (MEOLUTs) in the ‘L6’ band. Once these signals are detected and the beacons are located by the MEOLUTs, COSPAS-SARSAT Mission Control Centres (MCC) will receive the beacon location information and distribute the data to the relevant rescue centres worldwide.
Thanks to the work of European companies and state-of-the-art EU technology, the integration of Galileo into COSPAS-SARSAT improves the system by:
- Enabling nearly real-time detection and localisation of distress signals from anywhere in the world, significantly improving the latency between the beacon activation and distress localisation
- Making it easier to find the source of a signal by significantly boosting precision in comparison to the current situation
- Increasing availability and improving the detection of signals in difficult terrain or weather conditions thanks to multiple satellites
- Introducing a return link that the SAR operator can send back to the beacon to let people know that their distress signal has been received and a rescue mission has been initiated.
The SAR/Galileo infrastructure complies with the interoperability parameters defined by COSPAS-SARSAT. This enables the signals relayed by the SAR/Galileo, SAR/GPS or SAR/GLONASS infrastructure to be combined for detecting and locating beacons.
Galileo’s contribution to the MEOSAR system
In 2000, the USA, the European Commission and Russia began consultations with COSPAS-SARSAT on the feasibility of installing SAR repeater payloads on their Medium-Altitude Earth Orbit Navigation Satellite Systems (MEOSAR), and incorporating a 406 MHz MEOSAR capability into COSPAS-SARSAT. The USA MEOSAR programme is called SAR-GPS, the European programme is called SAR/Galileo, and the Russian programme is referred to as SAR/Glonass.
The initial investigations identified many possible SAR alerting benefits that might be realised from a MEOSAR system. These include:
- Near instantaneous global coverage with accurate independent location capability;
- Robust beacon to satellite communication links, high levels of satellite redundancy and availability;
- Resilience against beacon to satellite obstructions;
- The possible provision of additional (enhanced) SAR services.
Once fully operational, the MEOSAR system will offer the advantages of both the Low Earth Orbit Search and Rescue (LEOSAR) and the Geostationary Earth Orbit Search and Rescue (GEOSAR) systems without their current limitations. It will provide for the transmission of the distress message and the independent location of the beacon with near real-time worldwide coverage.
The large number of MEOSAR satellites that will be in orbit when the system is fully operational will allow each distress message to be relayed at the same time by several satellites to several ground antennas. This will improve the likelihood of detection and the accuracy of location determination.
What it means for you
With Galileo and the increased positioning accuracy it provides integrated into COSPAS-SARSAT, users will benefit from:
- a reduction in the time it takes to detect a person at sea or in the mountains from one hour to just 10 minutes after the distress beacon is activated
- improved localisation of the distress beacon from 10 km to less than 5 km
- increased availability
- better detection of signals in difficult terrain and weather conditions
- a return link that ensures users that their distress signal has been received and help is on the way (planned to be available end of 2018)
Want to find out more about?
If you would like to find out more about then don’t hesitate to get in touch with us today via info@mrtsos.com.
02/05/2018
Contact Us
Find Us
Marine Rescue Technologies Limited
Wescom Group,
Unit J1, Springfield Way,
Anlaby, HU10 6RJ

